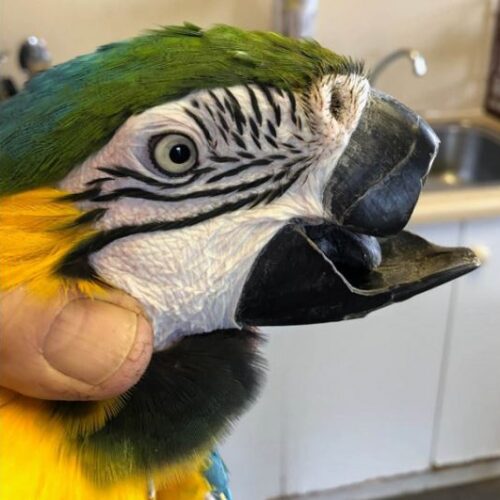
3D-Printed Beak Gives South African Macaw a New Lease on Life
Max, a 20-year-old blue and gold macaw, regains ability to eat solid food after groundbreaking prosthetic surgery.
Prof Alfred Ngowi
Exploring opportunities in South African research and innovation.
6 Innovative 3D Printed Solutions from Central University of Technology
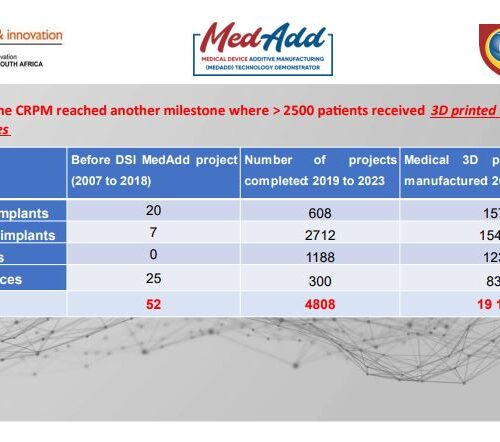
CRPM is not only addressing immediate healthcare needs but also building local capacity for medical device innovation and manufacturing in Africa.